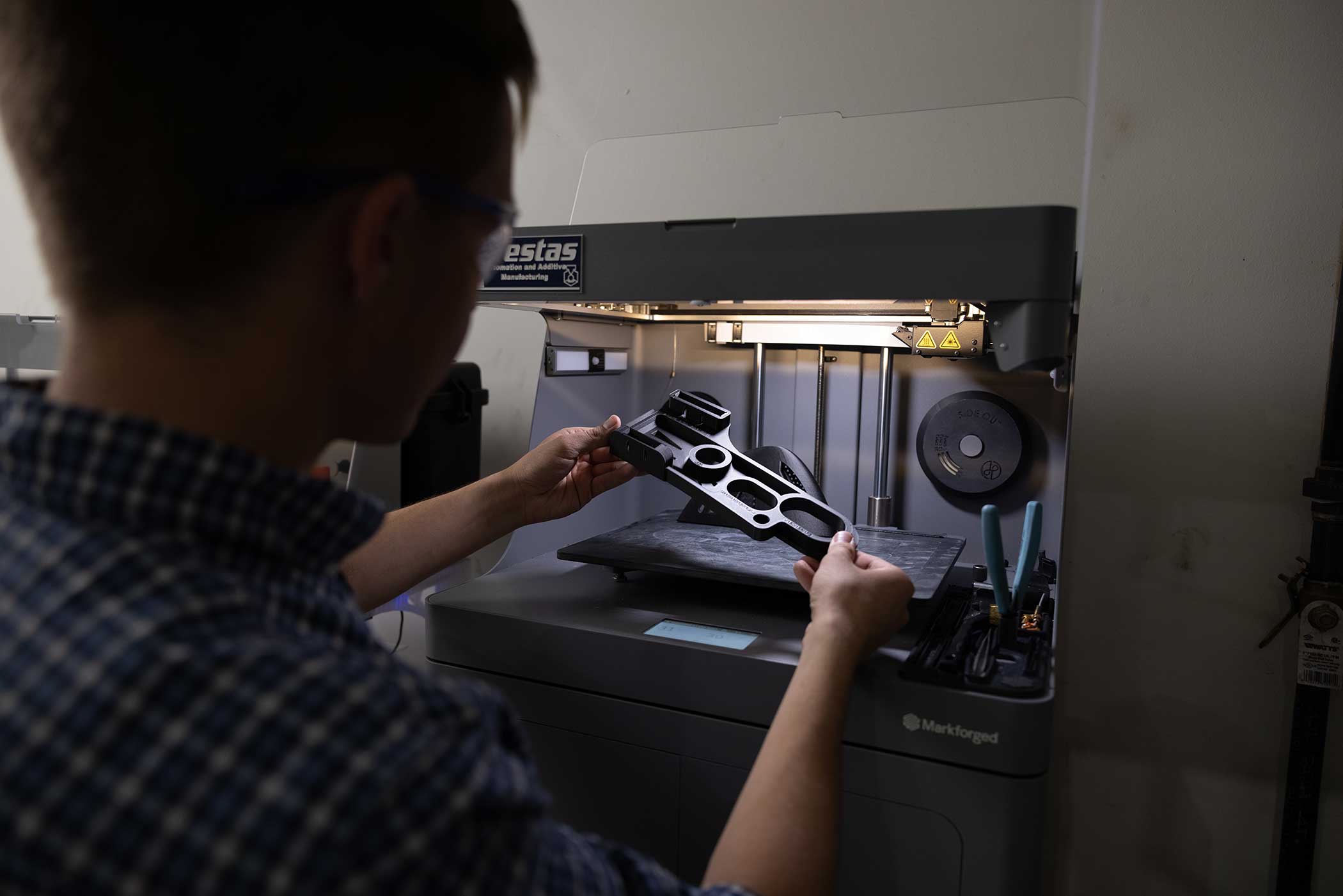

How data-driven 3D printers will change manufacturing
Machine learning can optimize hardware to increase printing speed and improve resolution
We all know the photos of Ford's production lines from 1920. But would we recognize them today? As part of a broader trend known as "Industry 4.0," the systems in many factories have undergone significant modernization in recent years. This digitalization of the manufacturing sector aims to leverage new technologies—such as cloud computing, intelligent automation, IoT devices, digital inventories, and data analytics—to help engineers make better decisions, improve factory processes, and ultimately require less human oversight.
At the heart of the digital transformation of the factory is additive manufacturing (AM), colloquially known as 3D printing, which enables the core technologies of Industry 4.0 to be applied directly to the manufacturing process itself. 3D printers have come a long way from their humble beginnings as rapid prototyping machines and gimmick factories for novelty items. They have evolved not only into machines that produce high-performance parts for aircraft, but also into data collection centers that collect vast amounts of information about how the various parts are manufactured during the manufacturing process.
Similar to how autonomous vehicles collect and apply data to continuously improve their driving capabilities, connected 3D printers can leverage the collected data for artificial intelligence-based automation. With each print job, 3D printers generate large amounts of data that are sent to and stored in the cloud. The print job data—ripe for AI, machine learning, and automation-based product features—can then be fed into algorithms accessible to printers and users via the cloud. This data helps companies make decisions about which parts to print and how best to print them, among other things, while improving the quality of print jobs.
AI comes into play
With the current state of manufacturing technology, AI can transform a hardware problem into a software solution. Machine learning can optimize hardware and automatically improve 3D printers through software updates to increase print speed and improve resolution. AI can help companies determine which parts, when produced in-house using additive manufacturing, will have the greatest impact on their bottom line. It can also connect to digital catalogs of existing parts and identify which specific parts are best suited for printing with different AM techniques.
By connecting to cloud software, 3D printers can use machine learning to automatically create tooling for printed parts. Manufacturers with more sophisticated AM skills apply AI-based optimizations during the design phase of new parts, simulating how a part's digital design will perform under specific loads after printing. AI is also used in artificial intelligence to detect print defects (and proactively pause printing if necessary) and to inspect parts during printing to ensure quality and compliance.
Similar to Tesla cars, the hardware in the field is constantly learning, improving, and becoming smarter with each update. As vendors improve the quality of the information collected during manufacturing and the way they capture data about how each 3D-printed part performs its task in the field, manufacturing technology is moving closer to a fully automated, closed-loop printing process. It can simply be presented with a real-world manufacturing problem to solve and then design and produce the part using the specific digital manufacturing technology that makes the most sense given the defined time, cost, and performance constraints.
This intelligent, self-contained automation of manufacturing takes a huge burden off manufacturers. The ability to automate part production—in a way that is both fast and reliable—significantly increases manufacturers' output and production speed. And while AM inherently streamlines the part manufacturing process, any clever application of the data collected by printers helps streamline certain points within the AM process. Engineers can step away from tedious manual tasks that are now automated—such as quality control and the manual design of tooling or fixtures for parts—and focus on innovation and solving more interesting problems. Machine operators can concentrate on producing the parts that either provide the greatest business value or can only be produced by machining.
Improving the supply chain
The biggest area where these data-driven 3D printers can make a difference? Manufacturers' global supply chains—where the inability to respond quickly and flexibly to ongoing disruptions often creates massive barriers to success. The adoption of just-in-time manufacturing processes has led to a world of fragile supply chains that were unable to keep pace as the pandemic's supply chain disruptions swept across the globe.
The year 2020 made this uncertainty clear.
The state of global supply chains hasn't improved much in the years since, and manufacturing in 2022 is still not for the faint of heart. While the complexity and general difficulties of sourcing parts and materials continue to lead to countless delays, shortages, and rising prices, this is a problem that is preventable with a few proactive measures—and the world is catching on. With the introduction of federal initiatives, such as the U.S. government's Additive Manufacturing Forward program, global supply chains are increasingly turning to 3D printing for short lead times and products that can be conveniently shipped to the desired location. However, the value of smart 3D printers to the supply chain is still relatively underappreciated. Smarter 3D printers are more precise and resilient; their closed-loop learning can add another layer of insurance against untimely delays and failures.
Given today's labor shortages, the newer intelligent automation features that vendors are bringing to market will likely also make 3D printing more attractive to labor-constrained manufacturers, driving AM adoption and ultimately stabilizing supply.
In addition, supporting human decisions in the critical problem-solving phases and fully automating many manual processes further reduces lead times for parts, in addition to the time saved through faster manufacturing and convenient logistics at the point of need.
The tip of the iceberg
As AI in 3D printing continues to advance, factory workflows are increasingly resembling the industry's vision of fully automated manufacturing.
Considering how intelligent AM addresses today's disrupted supply chains, one can imagine the impact of the smartest 3D printers yet to come. Fully automated design, manufacturing, and quality control of parts for specific problems will not only reduce the human resource requirements for addressing many acute supply chain issues to near zero and further reduce lead times. It will also uncover part designs that enable manufacturers to achieve the best performance and business return from every 3D-printed part, revealing designs that can solve the most challenging problems, comparable to the best engineering talent.
The adoption of additive manufacturing continues to grow to address current supply chain challenges. Along with additive manufacturing, Industry 4.0 technologies are pushing the boundaries of 3D printer capabilities and their benefits to businesses.
For the manufacturing industry, the future is clear. This open question should now prompt us to look inward.
Given the pace at which AI has taken hold in other industries, why has it taken so long for effective AI to reach manufacturing, and what's holding more manufacturers back from adopting these technologies faster and more widely? The answer may lie in the constant struggle between innovation and risk mitigation—a question that, when it comes to AI, could prove to be false dichotomies.
Learn more about the applications with the MarkTwo!
Which continuous filament is suitable for which application? How do I design correctly for filament 3D printing? What do users say about it, and where can I find more information? – You've come to the right place! We've listed several information sources that will help you get the answers you need.












Leave A Comment