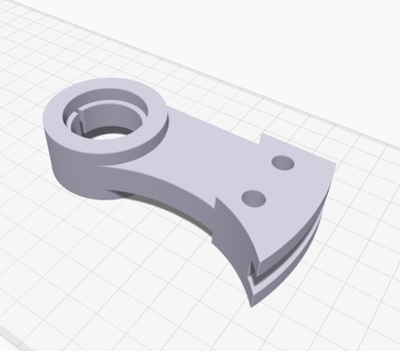
How to strengthen your 3D printed parts along the Z-axis
Sie wollen nicht, dass Ihre Teile brechen? Sehen Sie sich dieses Video an.
Wenn Du dich schon einmal mit 3D-Druck beschäftigt haben, hast Du wahrscheinlich schon gehört, dass die Z-Achse Vergleich zur XY-Ebene schwächer ist.
Das kann dazu führen, dass Teile brechen oder Risse bekommen, wenn hoher Druck oder Stöße ausgeübt werden.
Und wenn man darauf nicht vorbereitet sind, kann das den Tag oder Deine Pläne durcheinander bringen.
In diesem Video erfahren Sie, wie Sie Ihre 3D-gedruckten Teile so konstruieren, dass sie stabil genug sind, um die von Ihnen gewünschte Aufgabe zu erfüllen.
Lassen Sie es uns in den Kommentaren wissen, wenn es etwas gibt, das Sie gerne behandelt hätten, oder eine Herausforderung, die Sie gerade bewältigen!
Video-Kapitel
0:00 – Einführung
0:34 – Warum ist die Stärke der Z-Achse wichtig?
1:13 – Was ist Anisotropie?
2:41 – Was macht die z-Achse verwundbar?
5:43 – Anforderungen an die Funktion
6:39 – Biegewerkzeug-Demo
11:51 – Fazit
Request a DEMO component now!
See for yourself how strong the components are.

Learn more about 3D printing with continuous fibers!
Which continuous filament is suitable for which application? How do I design correctly for filament 3D printing? What do users say about it, and where can I find more information? – You've come to the right place! We've listed several information sources that will help you get the answers you need.








Hinterlasse einen Kommentar