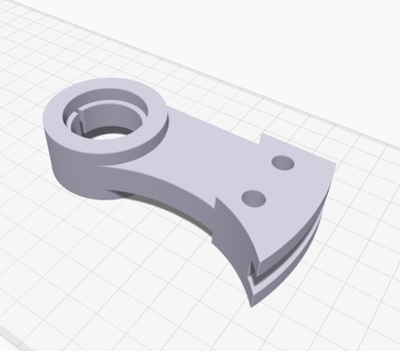
What is 3D printing?
[2 minutes reading time]
3D printing is a subset of additive manufacturing. In additive manufacturing, a part is made by adding material, while in subtractive manufacturing, a part is made by stripping material. In 3D printing, a 3D printer creates a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design (CAD) file. There are a variety of materials and technologies that make it easier than ever to create parts for all types of industries.
Many people assume that 3D printers are a new technology, although you may be surprised to know that these printers have been around since the 1980s. However, printers were mostly used for industrial purposes until 2009 and were too expensive for most people. Today, companies around the world can use 3D printers to produce parts for manufacturing purposes at a lower cost.
Users start with a CAD file, export it as an STL file and then upload it to the desired software. They can align the part to their requirements, then the software cuts the file into layers and starts printing. The part is printed layer by layer. Different technologies and materials determine how thick their part, the surface finish and the durability of the finished part can be, while the part size controls the printing time.
While 3D printing has often been associated with toys and hobby items, it is more than capable of producing parts that can withstand a variety of high-performance environments. You’ll find 3D printed parts used in industries such as manufacturing, energy and automotive. From functional prototypes, tools and fixtures to end-user parts, the 3D printing industry is revolutionizing several other industries and processes.
Learn more about 3D printing continuous fibres!
Which continuous fibre is suitable for which applications? How do I design correctly for filament 3D printing? What do users say and where can I find more information? – This is the right place for you! We listed some information leading you directly to the matching answers.