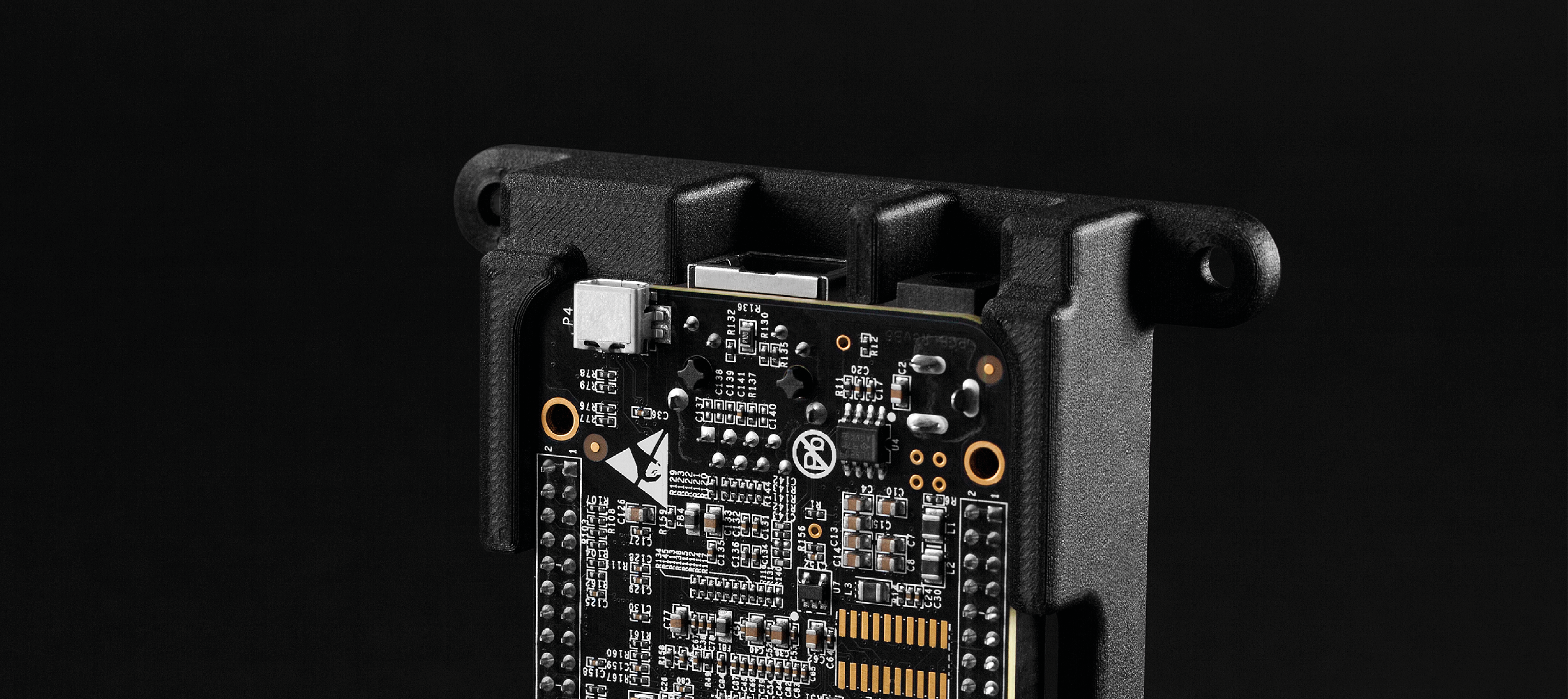
Introducing Onyx ESD!
08.12.2020: It is an exciting day as Markforged introduces their newest material, Onyx ESD, to all Markforged customers and the rest of the manufacturing world!
It took some extra iterations to nail it, but the reason we’re excited is that Markforged is releasing a truly differentiated, high-performance material that will change electronics manufacturing. Onyx ESD will allow electronics manufacturers to take advantage of the Digital Forge and the massive benefits it brings, even in applications with stringent ESD safety requirements necessary to avoid damage to sensitive electronics.
What is Onyx ESD?
Onyx ESD is a static-dissipative version of Onyx, Markforged’s popular micro carbon fiber filled nylon material that is used by customers to manufacture everything from prototypes, to tooling, to end-use parts. The addition of a precisely controlled quantity of conductive filler results in Onyx ESD meeting a tight surface resistance range that enables it to be used for a broad set of ESD sensitive applications. Onyx ESD can serve the full range of applications as a standalone material or — when maximum strength or stiffness is desired — reinforced with continuous fiber.
Nearly every electronic product you use on a daily basis was built in an ESD-safe environment using ESD-safe tooling. Onyx ESD enables manufacturers to print this tooling on-demand using Markforged Industrial 3D printers, reducing costs and lead time versus traditional processes, while at the same time reducing inventory. And for large enterprises, these parts can be digitally distributed across a global fleet, allowing for rapid response to changing production demands at the speed of software.
Why Markforged Onyx ESD?
What makes Onyx ESD special is its tight surface resistance range. Surface resistance is a spectrum. On one end there are “conductive” materials, like copper, aluminum, and other metals that easily flow electricity. On the other end are “insulative” materials like wood or most plastics that hardly flow electrons at all. Conductive materials make it easy for sparks to jump and cause damage. Insulative materials build-up charge which can then easily jump somewhere it shouldn’t and cause damage. The goldilocks zone is the “Dissipative” range which allows for a controlled flow of electrons so they don’t build up and jump nor facilitate sparks through a conductive path. This is the range Markforged targeted for Onyx ESD and ultimately ended up significantly tighter than.
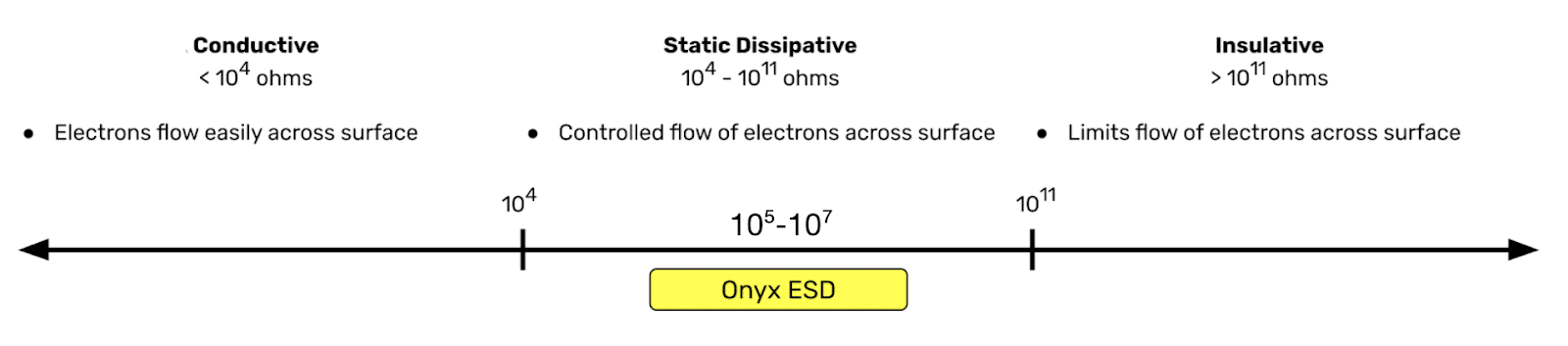
While anything between 104 and 1011 ohms of surface resistance is considered static dissipative, Markforged has demonstrated that Onyx ESD, when printed on their Industrial printers, achieves between 105 and 107 ohms. This is across multiple part orientations (top, bottom, side, and 45 degrees) and multiple material lots. This tight range is only possible because of the precise material formulation of Onyx ESD and the superior print quality of the Industrial series printers. But those aren’t the only reasons Onyx ESD is special. It’s also strong — stronger than Onyx in fact — and prints with exceptional surface finish.
Applications for Onyx ESD
Onyx ESD is best suited for tooling, jigs, and fixtures that must be ESD-safe and for parts that cause processing difficulties when charge builds up. Some examples include assembly fixtures, test fixtures, custom hand tools, enclosures, component trays, and robotic end-of-arm grippers.
One Beta customer that develops testing equipment for large electronics manufacturers has been using Onyx ESD in their customer-facing test fixtures. They historically used CNC machining, but it limited the geometric freedom they could achieve with parts. They also tried 3D printed ESD parts from other companies but the accuracy and surface quality was poor and not acceptable for delivery to customers.
Request a demo!
Feel the strength of continuous fiber for yourself.

Learn more about 3D printing continuous fibres!
Which continuous fibre is suitable for which applications? How do I design correctly for filament 3D printing? What do users say and where can I find more information? – This is the right place for you! We listed some information leading you directly to the matching answers.







Leave A Comment